Guide on Man-Created Diamonds - Buying Tips, Types & Process
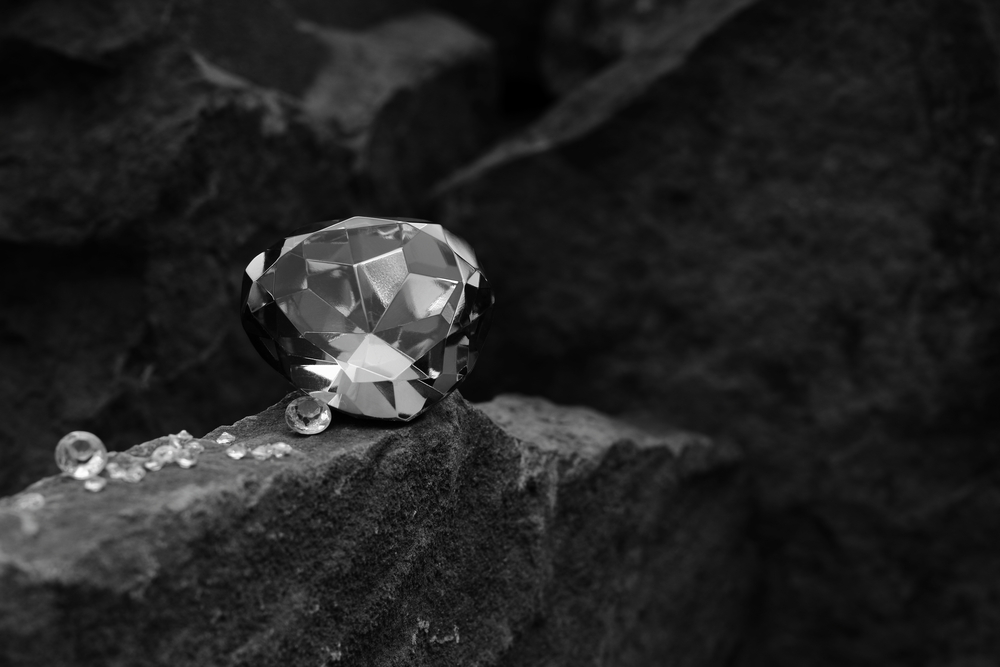


In the last couple of decades, technology has revolutionized nearly every industry. 3D printers are producing food, and robots and software are doing tasks that humans handled for hundreds of years. In such an age, it isn’t surprising that man is producing diamonds in laboratories. And these are “real diamonds”.
As interest and inclination towards man-made diamonds, lab-grown diamonds, or cultured diamonds are growing, a number of factors have supported and boosted their preferment. Recently, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States has changed the definition of diamonds in its jewelry guidelines by removing the word ‘natural’. This further reinforces the position of lab-grown diamonds as real diamonds.
Moreover, known brands and diamond sellers have recognized the preferred choice of conscious consumers, which has made them offer consumers more lab-grown diamonds. Today, given a choice, man-made diamonds are preferred over their mined counterparts.
What are man-made diamonds?
Man-made diamonds are those that are created or grown by scientific processes in laboratories. As opposed to natural diamonds that are created by geological processes, man-made diamonds are produced with the help of technological processes that are of the exact same composition as those that produce diamonds beneath the Earth.
Laboratory diamonds are real. They are not the same as a cubic zirconia or a moissanite stone. These two are stimulants, which means they look like real man-made diamonds but are softer and have different optical properties when compared to real diamond.
How Are Diamonds Created in Labs?
Diamonds are created in labs with high-tech machinery and scientific processes. There are two main processes: high pressure high temperature (HPHT) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Here’s how it works:
-
First, experts select the finest-quality diamond seeds, which are carefully placed on a metal disk.
-
The disk is then placed inside the diamond-growing reactor of the machine.
-
Next, the seeds go through various processes over 10 to 12 weeks.
-
A combination of gases, pressure, and temperature creates an environment that allows carbon atoms to break down and rain upon the seeds.
-
Atom-by-atom, the seeds transform into rough diamonds. These rough diamonds have the same chemical, physical, and optical properties as mined diamonds.
- The rough diamonds are cut and polished to exacting standards in high-tech factories.
Types of Man-Made Diamonds
Diamonds naturally occur in different types: Type 1 (a/b) or Type 2 (a/b). The purest form of diamond is Type 2a, which has no impurities and is colorless. Less than 2% of mined diamonds are Type 2A diamonds, while all lab-grown diamonds are Type 2a.
Key Factors to Consider When Purchasing Man-Made Diamonds
Diamond simulants look exactly the same as real diamonds to the naked eye. It is important to observe some key aspects of lab-grown real diamonds at the time of purchase.
- The process used to create lab-grown diamonds: Man-made diamonds always have accurate information about the process with which they were made, inscribed on the diamonds. Diamonds are made with two processes: HPHT and CVD. If a diamond does not have accurate information about the process by which it was made, then it could be a simulant.
- Certification: Another important thing to look out for is the certification of the diamond by IGI (International Gemological Institution). Consumers must insist on the certification when buying their diamonds. Sellers must make sure that they provide a certificate when selling a diamond. Obtaining a certificate enables transparency, confidence, and trust between buyers and sellers, as well as authentication. In many cases, even if the diamond has a certificate, it is important to buy the diamond from an accredited seller who can verify the accuracy of the certificate.
How and Where Are Lab-Grown Diamonds Certified?
Man-made diamonds are certified by the IGI (International Gemological Institution). These certificates protect buyers and sellers of lab-grown diamonds by setting and maintaining the standards used to evaluate the quality of the diamonds. Consumers can be assured and confident about their purchase when certificates accompany their diamonds. The certificates carry accurate grading of the diamonds based on the 4 Cs.
Why Are Created Diamonds Considered Better Than Mined Ones?
Real. Pure. Beautiful. Affordable. Precious. Loose lab-grown diamonds have all the qualities that consumers want in their diamonds. Besides these obvious strengths, man-made diamonds have several other strong points. Here are some:
-
Lab-created diamonds have the same physical hardness and strength as mined diamonds.
-
Lab-grown diamonds have the same optical properties as minded diamonds.
-
Diamonds grown in a laboratory have the same molecular structure as minded diamonds.
-
Real man-made diamonds do not have any fluorescence.
-
Lab-grown diamonds are around 30% cheaper than mined diamonds.
-
Loose man-made diamonds are often cleaner and have fewer inclusions.
-
Lab diamonds are certified as real diamonds with laser inscriptions by forensic laboratories.
-
Man-made diamonds can meet high market demands.
-
Lab-grown diamonds are not harmful to the earth and the environment.
-
Man-made diamonds are not conflict or blood diamonds. They are ethically produced in safe environments.
- Lab-created diamonds can be customized.
As producers of mined diamonds struggle to stress on the “real is rare” belief, the lab-grown diamonds industry is already winning the hearts of conscious and aware diamond connoisseurs and a growing young population that is taking a liking to the man-made sparklers. And why not?

{"AutoID":11,"DateCreation":"\/Date(1605034385110)\/","DateModified":"\/Date(1749814553903)\/","CreatedBy":null,"ModifiedBy":"Rahul Bohra ","RecordStatus":"A","Title":"Guide on Man-Created Diamonds - Buying Tips, Types \u0026 Process","SubTitle":"In the last couple of decades, technology has taken over practically every industry. 3D printers are producing food; and robots and software are doing tasks that were being by humans for hundreds of years...","Description":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eIn the last couple of decades, technology has revolutionized nearly every industry. 3D printers are producing food, and robots and software are doing tasks that \u0026nbsp;humans handled for hundreds of years. In such an age, it isn\u0026rsquo;t surprising that man is producing diamonds in laboratories. And these are \u0026ldquo;real diamonds\u0026rdquo;.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u0026nbsp;\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eAs interest and inclination towards\u0026nbsp;man-made diamonds, lab-grown diamonds, or\u0026nbsp;\u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/what-are-cultured-diamonds-and-should-you-buy-them/\"\u003ecultured diamonds\u003c/a\u003e\u0026nbsp;are growing, a number of factors have supported and boosted their preferment. Recently, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States has changed the definition of diamonds in its jewelry guidelines by removing the word \u0026lsquo;natural\u0026rsquo;. This further reinforces the position of\u0026nbsp;lab-grown diamonds\u0026nbsp;as real diamonds.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003e\u0026nbsp;\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003eMoreover, known brands and diamond sellers have recognized the preferred choice of conscious consumers, which has made them offer consumers more lab-grown diamonds. Today, given a choice,\u0026nbsp;man-made diamonds\u0026nbsp;are preferred over their mined counterparts.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003e\u0026nbsp;\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003ch2\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eWhat are man-made diamonds?\u003c/strong\u003e\u003c/h2\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eMan-made diamonds\u0026nbsp;are those that are created or grown by scientific processes in laboratories. As opposed to natural diamonds that are created by geological processes, man-made diamonds are produced with the help of technological processes that are of the exact same composition as those that produce diamonds beneath the Earth.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u0026nbsp;\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003e\u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/types-of-lab-grown-diamonds/\"\u003eLaboratory diamonds\u0026nbsp;\u003c/a\u003eare real. They are not the same as a \u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/man-made-diamonds-vs.-cubic-zirconia-what-is-the-difference/\"\u003ecubic zirconia\u003c/a\u003e or a moissanite stone. These two are stimulants, which means they look like real man-made diamonds but are softer and have different optical properties when compared to real diamond.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003e\u0026nbsp;\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003ch2\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eHow Are Diamonds Created in Labs?\u003c/strong\u003e\u003c/h2\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003eDiamonds are created in labs with high-tech machinery and scientific processes. There are two\u0026nbsp;main processes:\u0026nbsp;\u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/hpht-lab-grown-diamonds-history-process-and-benefits/\"\u003ehigh pressure high temperature\u003c/a\u003e (\u003cstrong\u003eHPHT\u003c/strong\u003e)\u0026nbsp;and\u0026nbsp;\u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/cvd-diamonds-everything-you-need-to-know/\"\u003echemical vapor deposition\u003c/a\u003e (\u003cstrong\u003eCVD\u003c/strong\u003e). Here\u0026rsquo;s how it works:\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cul\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eFirst, experts select the finest-quality diamond seeds, which are carefully placed on a metal disk.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eThe disk is then placed inside the diamond-growing reactor of the machine.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eNext, the seeds go through various processes over 10 to 12 weeks.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eA combination of gases, pressure, and temperature creates an environment that allows carbon atoms to break down and rain upon the seeds.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eAtom-by-atom, the seeds transform into rough diamonds. These rough diamonds have the same chemical, physical, and optical properties as mined diamonds.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli\u003eThe rough diamonds are cut and polished to exacting standards in high-tech factories.\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\u003c/ul\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003ch2\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eTypes of Man-Made Diamonds\u003c/strong\u003e\u003c/h2\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003eDiamonds naturally occur in different types:\u0026nbsp;Type 1 (a/b) or Type 2 (a/b). The purest form of diamond is Type 2a, which has no impurities and is colorless. Less than 2% of mined diamonds are\u0026nbsp;\u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/what-is-a-type-iia-lab-grown-diamond/\"\u003eType 2A diamonds\u003c/a\u003e, while all lab-grown diamonds are Type 2a.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003e\u0026nbsp;\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003ch2\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eKey Factors to Consider When Purchasing Man-Made Diamonds\u003c/strong\u003e\u003c/h2\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003eDiamond simulants look\u0026nbsp;exactly the same as real diamonds to the naked eye. It is important to observe some key aspects of\u0026nbsp;lab-grown real diamonds\u0026nbsp;at the time of purchase.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cul\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eThe process used to create lab-grown diamonds:\u003c/strong\u003e\u0026nbsp;Man-made diamonds always have accurate information about the process with which they were made, inscribed on the diamonds. Diamonds are made with two processes: HPHT and CVD. If a diamond does not have accurate information about the process by which it was made, then it could be a simulant.\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eCertification\u003c/strong\u003e: Another important thing to look out for is the certification of the diamond by IGI (International Gemological Institution). Consumers must insist on the certification when buying their diamonds. Sellers must make sure that they provide a certificate when selling a diamond. Obtaining a certificate enables transparency, confidence, and trust between buyers and sellers, as well as authentication. In many cases, even if the diamond has a certificate, it is important to buy the diamond from an accredited seller who can verify the accuracy of the certificate.\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\u003c/ul\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003ch2\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eHow and Where Are Lab-Grown Diamonds Certified?\u003c/strong\u003e\u003c/h2\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003eMan-made diamonds are certified by the \u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/are-igi-certified-lab-grown-diamonds-legit/\"\u003eIGI\u003c/a\u003e (International Gemological Institution). These certificates protect buyers and sellers of lab-grown diamonds by setting and maintaining the standards used to evaluate the quality of the diamonds. Consumers can be assured and confident about their purchase when certificates accompany their diamonds. The certificates carry accurate grading of the diamonds based on the \u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/the-4cs-of-diamond-grading-all-you-need-to-know/\"\u003e4 Cs\u003c/a\u003e.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003e\u0026nbsp;\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003ch2\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eWhy Are Created Diamonds Considered Better Than Mined Ones?\u003c/strong\u003e\u003c/h2\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003eReal. Pure. Beautiful. Affordable. Precious.\u0026nbsp;\u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/tips-while-buying-loose-lab-created-diamonds-online/\"\u003eLoose lab-grown diamonds\u0026nbsp;\u003c/a\u003ehave all the qualities that consumers want in their diamonds. Besides these obvious strengths, man-made diamonds have several other strong points. Here are some:\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cul\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp\u003e\u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/how-are-lab-created-diamonds-made/\"\u003eLab-created diamonds\u003c/a\u003e\u0026nbsp;have the same physical hardness and strength as mined diamonds.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eLab-grown diamonds have the same optical properties as \u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/can-you-easily-distinguish-between-a-mined-and-a-lab-grown-diamond/\"\u003eminded diamonds\u003c/a\u003e.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/facts-about-lab-grown-diamonds/\"\u003eDiamonds grown in a laboratory\u0026nbsp;\u003c/a\u003ehave the same molecular structure as minded diamonds.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eReal man-made diamonds\u0026nbsp;do not have any fluorescence.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/types-of-lab-grown-diamonds/\"\u003eLab-grown diamonds\u003c/a\u003e are around 30% cheaper than mined diamonds.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eLoose man-made diamonds are often cleaner and have fewer inclusions.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eLab diamonds are\u0026nbsp;certified as real diamonds\u0026nbsp;with laser inscriptions by forensic laboratories.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eMan-made diamonds can meet high market demands.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eLab-grown diamonds are not harmful to the earth and the environment.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\r\n\t\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003eMan-made diamonds are not conflict or \u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/why-are-lab-created-diamonds-called-blood-free-diamonds/\"\u003eblood diamonds\u003c/a\u003e. They are ethically produced in safe environments.\u003c/p\u003e\r\n\t\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\t\u003cli\u003eLab-created diamonds\u0026nbsp;can be customized.\u003c/li\u003e\r\n\u003c/ul\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003cp\u003eAs producers of mined diamonds struggle to stress on the \u0026ldquo;real is rare\u0026rdquo; belief, the \u003ca href=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/the-future-of-lab-created-diamond-industry-seems-shining-bright/\"\u003elab-grown diamonds industry\u003c/a\u003e is already winning the hearts of conscious and aware diamond connoisseurs and a growing young population that is taking a liking to the man-made sparklers. And why not?\u003c/p\u003e\r\n","FromDate":null,"ToDate":null,"Image_Url":"man-made-diamonds-are-the-future-heres-why.jpg","Image_Alt":"Future of Man-Made Diamonds","KeyWords":"conflict free diamonds, man made diamonds, best man made diamonds, buy conflict free diamonds, man made diamonds for sale, buy man made diamonds, grown diamond corporation , lab grown diamonds , lab diamonds , lab made diamonds , synthetic diamonds , best lab grown diamonds","MetaDescription":"The future of lab-grown diamonds is bright. Lab-grown diamonds have been ruling the diamond market for quite some time now. Browse now to understand all about lab grown diamonds.","MetaTitle":"Guide on Man-Created Diamonds - Buying Tips, Types \u0026 Process","CanonicalLink":"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/man-made-diamonds-are-the-future-heres-why/","MetaContent":"\u003c!-- Open Graph / Facebook --\u003e\r\n\u003cmeta property=\"og:type\" content=\"article\"\u003e\r\n\u003cmeta property=\"og:url\" content=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/lab-grown-diamonds-are-redefining-modern-jewelry-heres-how/\"\u003e\r\n\u003cmeta property=\"og:title\" content=\"Lab Grown Diamond Jewellery in Trend | Grown Diamond Corporation\"\u003e\r\n\u003cmeta property=\"og:description\" content=\"Here you can learn about the popularity of lab-grown diamonds diamonds modern jewelry market and the many reasons why consumers are interested in buying lab-grown diamonds. Read more!\"\u003e\r\n\u003cmeta property=\"og:image\" content=\"https://docs.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/man-made-diamonds-are-the-future-heres-why.jpg\"\u003e\r\n\r\n\u003c!-- Twitter --\u003e\r\n\u003cmeta name=\"twitter:card\" content=\"summary_large_image\"\u003e\r\n\u003cmeta name=\"twitter:url\" content=\"https://www.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/lab-grown-diamonds-are-redefining-modern-jewelry-heres-how/\"\u003e\r\n\u003cmeta name=\"twitter:title\" content=\"Lab Grown Diamond Jewellery in Trend | Grown Diamond Corporation\"\u003e\r\n\u003cmeta name=\"twitter:description\" content=\"Here you can learn about the popularity of lab-grown diamonds diamonds modern jewelry market and the many reasons why consumers are interested in buying lab-grown diamonds. Read more!\"\u003e\r\n\u003cmeta name=\"twitter:image\" content=\"https://docs.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/man-made-diamonds-are-the-future-heres-why.jpg\"\u003e\r\n","SeqNo":26,"Slug":"man-made-diamonds-are-the-future-heres-why","GetTitle":"guide-on-man-created-diamonds-buying-tips-types-process","GetImageUrl":"https://docs.growndiamondcorp.com/blog/man-made-diamonds-are-the-future-heres-why.jpg"}
© 2025 Grown Diamond Corporation - Lab Grown Diamonds. All rights reserved.| Sitemap